 “Several studies support, both in vitro and in vivo, the anti-cancer effects of cannabidiol (CBD), a transient receptor potential vanilloid 2 (TRPV2) ligand. TRPV2, often dysregulated in tumors, is associated with altered cell proliferation and aggressiveness.
“Several studies support, both in vitro and in vivo, the anti-cancer effects of cannabidiol (CBD), a transient receptor potential vanilloid 2 (TRPV2) ligand. TRPV2, often dysregulated in tumors, is associated with altered cell proliferation and aggressiveness.
Endometrial cancer (EC) is historically divided in type I endometrioid EC and type II non-endometrioid EC, associated with poor prognosis. Treatment options with chemotherapy and combinations with radiation showed only limited efficacy. Since no data are reported concerning TRPV2 expression as well as CBD potential effects in EC, the aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of TRPV2 in biopsies and cell lines as well as the effects of CBD in in vitro models. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), cell viability, migration, and chemo-resistance have been evaluated.
Results show that TRPV2 expression increased with the malignancy of the cancer tissue and correlated with shorter PFS (p = 0.0224). Moreover, in vitro TRPV2 over-expression in Ishikawa cell line increased migratory ability and response to cisplatin. CBD reduced cell viability, activating predominantly apoptosis in type I cells and autophagy in mixed type EC cells. The CBD improved chemotherapeutic drugs cytotoxic effects, enhanced by TRPV2 over-expression. Hence, TRPV2 could be considered as a marker for optimizing the therapy and CBD might be a useful therapeutic option as adjuvant therapy.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32751388/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/15/5409

 “Multidrug resistance (MDR) to known chemotherapeutic agents is increasing while the development of new drugs is lacking behind. Combination therapies might increase the development of effective treatment.
“Multidrug resistance (MDR) to known chemotherapeutic agents is increasing while the development of new drugs is lacking behind. Combination therapies might increase the development of effective treatment.


 “Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
“Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.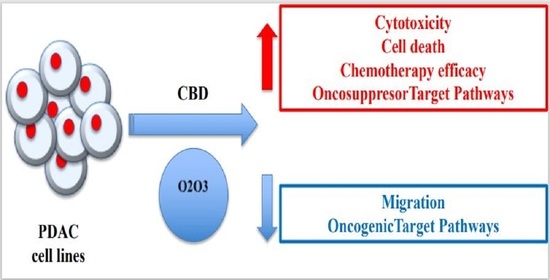
 “∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
“∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system. “Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC.
“Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC. “This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis.
“This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis. “The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.
“The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.
 “The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search.
“The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search.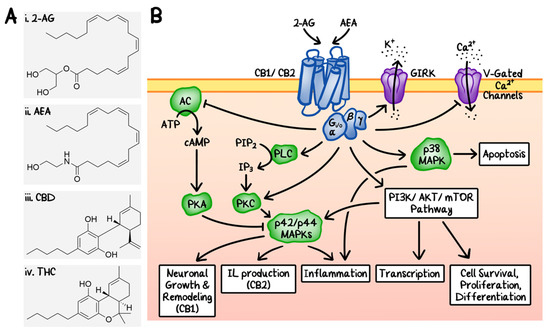
 “Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects.
“Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects. “Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies.
“Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies. “Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
“Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.