“Olivia Newton-John says medicinal marijuana is a key part of her treatment for stage four cancer. In an exclusive interview with 60 Minutes reporter Liz Hayes, Newton-John says that not only has cannabis assisted with her pain management, sleep and anxiety – but it’s having affects on her physical health too. “I’m incredibly pro cannabis,” she told Liz Hayes. “If I don’t take the cannabis, I can feel the pain so I know it’s working.”
“Olivia Newton-John: ‘Medicinal cannabis enhanced my quality of life’. For this special 60 Minutes report, Olivia Newton-John tells Liz Hayes that despite her latest diagnosis she was “getting strong again” and that her quality of life had been greatly enhanced by medicinal cannabis, grown for her by her husband John. Olivia and John are strong believers in the power of plants particularly cannabis. “I really believe the cannabis has made a huge difference,” says Olivia. “I’m confident,” John concurs. Olivia, John and Chloe are now cannabis converts, and now want medicinal cannabis legalised as an alternative treatment in Australia.” https://www.9news.com.au/national/olivia-newton-john-60-minutes-medical-cannabis-advocate-after-cancer-treatment-news/da315271-7387-47e0-a14e-c7fbb9a4b18b
“I have to credit again my wonderful husband because he gives me Cannabis oil that he makes for me, grows the plants here. We’re so lucky in California that we can grow our own, and so he’s made me these incredible tinctures that help with my pain and with sleep, and everything.” https://www.today.com/
 “There is a growing preference for the use of
“There is a growing preference for the use of  “Pancreatic cancer is particularly refractory to modern therapies, with a 5-year survival rate for patients at a dismal 8%.
“Pancreatic cancer is particularly refractory to modern therapies, with a 5-year survival rate for patients at a dismal 8%. “Marijuana has been used by many different civilizations for numerous different purposes, including its use for medical indications. Recently, there has been significant media coverage of the efficacy of medical marijuana in the treatment of seizures in children with Dravet syndrome, and this has led many to search for other possible pediatric indications for cannabinoids, including many different indications in pediatric cancer. However, there is very little evidence on safety or efficacy of cannabinoids in children being treated with cancer. This commentary accompanies a recent paper by a group in Israel who have published their experience of medical marijuana in 50 children and adolescents with cancer, showing excellent satisfaction and better symptom control, and without significant adverse drug reactions. This study from Israel is an excellent first step, but prospective well-designed trials of medical marijuana in pediatric oncology are urgently needed.”
“Marijuana has been used by many different civilizations for numerous different purposes, including its use for medical indications. Recently, there has been significant media coverage of the efficacy of medical marijuana in the treatment of seizures in children with Dravet syndrome, and this has led many to search for other possible pediatric indications for cannabinoids, including many different indications in pediatric cancer. However, there is very little evidence on safety or efficacy of cannabinoids in children being treated with cancer. This commentary accompanies a recent paper by a group in Israel who have published their experience of medical marijuana in 50 children and adolescents with cancer, showing excellent satisfaction and better symptom control, and without significant adverse drug reactions. This study from Israel is an excellent first step, but prospective well-designed trials of medical marijuana in pediatric oncology are urgently needed.” “Over the course of the last decade, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) have been identified as part of the
“Over the course of the last decade, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) have been identified as part of the  “Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug.
“Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug.
 “Mixtures of different Cannabis sativa phytocannabinoids are more active biologically than single phytocannabinoids. However, cannabis terpenoids as potential instigators of phytocannabinoid activity have not yet been explored in detail.
“Mixtures of different Cannabis sativa phytocannabinoids are more active biologically than single phytocannabinoids. However, cannabis terpenoids as potential instigators of phytocannabinoid activity have not yet been explored in detail. “Phytocannabinoids are unique terpenophenolic compounds predominantly produced in the glandular trichomes of the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa L.). The delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main active constituent responsible for the plant’s psychoactive effect and, together with the non- psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD), the most investigated naturally occurring cannabinoid.
“Phytocannabinoids are unique terpenophenolic compounds predominantly produced in the glandular trichomes of the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa L.). The delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main active constituent responsible for the plant’s psychoactive effect and, together with the non- psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD), the most investigated naturally occurring cannabinoid. “Ovarian cancer, with over a 90% reoccurrence within 18 months of treatment, and approximately a 30% mortality rate after 5 years, is the leading cause of death in cases of gynaecological malignancies. Acquired resistance, and toxic side effects by clinically used agents are major challenges associated with current treatments, indicating the need for new approaches in ovarian cancer treatment.
“Ovarian cancer, with over a 90% reoccurrence within 18 months of treatment, and approximately a 30% mortality rate after 5 years, is the leading cause of death in cases of gynaecological malignancies. Acquired resistance, and toxic side effects by clinically used agents are major challenges associated with current treatments, indicating the need for new approaches in ovarian cancer treatment. “Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of polar extracts of edible resources from Fedora hemp cultivar (Cannabis sativa L.), namely seed, flour and oil, were evaluated. The main components in the polar extracts were identified using HPLC-DAD and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS. As expected, the molecular profile of components from seeds and flour was strictly similar, dominated by N-trans-caffeoyltyramine. The profile of oil polar extracts contained hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives and
“Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of polar extracts of edible resources from Fedora hemp cultivar (Cannabis sativa L.), namely seed, flour and oil, were evaluated. The main components in the polar extracts were identified using HPLC-DAD and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS. As expected, the molecular profile of components from seeds and flour was strictly similar, dominated by N-trans-caffeoyltyramine. The profile of oil polar extracts contained hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives and  “Cannabinoid receptors have been detected in human gliomas and cannabinoids have been proposed as novel drug candidates in the treatment of brain tumors.
“Cannabinoid receptors have been detected in human gliomas and cannabinoids have been proposed as novel drug candidates in the treatment of brain tumors. “Cancer patients experience multiple symptoms throughout their illness, and some report benefit from the use of cannabis. There are concerns that many patients are accessing products inappropriate for their situation and potentially putting themselves at risk.
“Cancer patients experience multiple symptoms throughout their illness, and some report benefit from the use of cannabis. There are concerns that many patients are accessing products inappropriate for their situation and potentially putting themselves at risk. “Indisputably, cancer is a global crisis that requires immediate intervention. Despite the use of conventional treatments over the past decades, it is acceptable to admit that these are expensive, invasive, associated with many side effects and, therefore, a reduced quality of life.
“Indisputably, cancer is a global crisis that requires immediate intervention. Despite the use of conventional treatments over the past decades, it is acceptable to admit that these are expensive, invasive, associated with many side effects and, therefore, a reduced quality of life.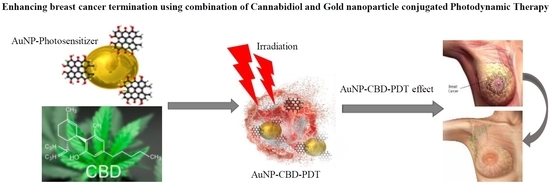
 “The endogenous lipid metabolism network is associated with the occurrence and progression of malignancies.
“The endogenous lipid metabolism network is associated with the occurrence and progression of malignancies. “Little is known about the endocannabinoid (eCB) system in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue (SCCOT). Here we have investigated, at the mRNA level, expression of genes coding for the components of the eCB system in tumour and non-malignant samples from SCCOT patients. Expression of NAPEPLD and PLA2G4E, coding for eCB anabolic enzymes, was higher in the tumour tissue than in non-malignant tissue. Among genes coding for eCB catabolic enzymes, expression of MGLL was lower in tumour tissue while PTGS2 was increased. It is concluded that the eCB system may be dysfunctional in SCCOT.”
“Little is known about the endocannabinoid (eCB) system in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue (SCCOT). Here we have investigated, at the mRNA level, expression of genes coding for the components of the eCB system in tumour and non-malignant samples from SCCOT patients. Expression of NAPEPLD and PLA2G4E, coding for eCB anabolic enzymes, was higher in the tumour tissue than in non-malignant tissue. Among genes coding for eCB catabolic enzymes, expression of MGLL was lower in tumour tissue while PTGS2 was increased. It is concluded that the eCB system may be dysfunctional in SCCOT.”
 “Grade IV glioblastoma multiforme is a deadly disease, with a median survival of around 14 to 16 months. Maximal resection followed by adjuvant radiochemotherapy has been the mainstay of treatment since many years, although survival is only extended by a few months. In recent years, an increasing number of data from in vitro and in vivo research with cannabinoids, particularly with the non-intoxicating cannabidiol (CBD), point to their potential role as tumour-inhibiting agents. Herein, a total of nine consecutive patients with brain tumours are described as case series; all patients received CBD in a daily dose of 400 mg concomitantly to the standard therapeutic procedure of maximal resection followed by radiochemotherapy. By the time of the submission of this article, all but one patient are still alive with a mean survival time of 22.3 months (range=7-47 months). This is longer than what would have been expected.”
“Grade IV glioblastoma multiforme is a deadly disease, with a median survival of around 14 to 16 months. Maximal resection followed by adjuvant radiochemotherapy has been the mainstay of treatment since many years, although survival is only extended by a few months. In recent years, an increasing number of data from in vitro and in vivo research with cannabinoids, particularly with the non-intoxicating cannabidiol (CBD), point to their potential role as tumour-inhibiting agents. Herein, a total of nine consecutive patients with brain tumours are described as case series; all patients received CBD in a daily dose of 400 mg concomitantly to the standard therapeutic procedure of maximal resection followed by radiochemotherapy. By the time of the submission of this article, all but one patient are still alive with a mean survival time of 22.3 months (range=7-47 months). This is longer than what would have been expected.”